How are Code Signing Certificates Different from Email Signing Certificates?
Safety is everything, especially in a time when everything has gone digital. Therefore, people must stay cautious whenever they download any software from the internet. It will ensure that the file is downloaded from an authentic source and not any third party pretending to be the original source. How is that possible, you ask? The answer is a code signing certificate! Code signing certificates help your customers know that you are the official publisher of the code and there has been no tampering by third parties since you signed it.
The importance of code signing certificates is quite high in the software development industry. However, the newcomers often question whether it is any different from the other certificates. An example can be the differentiation between a document signing certificate and code signing certificate. In any case, the debacle of Code Signing Certificate Vs. Email Signing Certificate keeps coming every now and then. The visible confusion is also witnessed in Stack Overflow. It is one of the biggest names in the digital communities. If confusion occurs in such a knowledgeable community, it is about time we clear the air around it.
So, let us begin with it already.
Before differentiating between the two, we will talk about what the terms mean and if there is any kind of similarity that makes them synonymous with each other, then we will shed light on what separates them from each other.
What are Code Signing Certificates?
Simply put, a code signing certificate can be defined as a certificate that ensures that a particular piece of executable file, software, code, or application, is not subjected to tampering by any third party since the software owner/publisher signed it.
In other words, it can be considered as a solid proof that allows the recipient to identify the source while ensuring that the particular piece of software is not opened or modified since its signature.
The working of a code signing certificate goes something like this: a certificate is sent by a trusted and reliable certificate authority. The authority is responsible for verifying the authenticity of the sender and then issues a certificate. Upon seeing the certificate, end-users can rely on the organization that has created the software.
Perhaps a picture will help you understand better. So below is the picture showing two software (one code signed and one does not code signed) being installed:
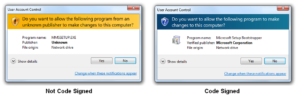
Oftentimes the browser simply proceeds without asking for the consent of the users. In this case, you can stay assured that the software is signed from a reliable certificate. When you buy a Code Signing Certificate, the browser trusts the download. Also, did you know that the browser can perform a check in the background where it verifies the integrity of the downloaded file? Yes, that is possible.
For public trust usage, code signing certificates are available in two types. Let us see what they are:
What are the types of Code Signing Certificates?
Organization Validation (OV) or Standard Certificate
Organization Validation Code Signing Certificates are for developers who want to sign code as an organization instead of an individual. For getting this certificate, the Certificate Authority will verify that your business or company is a legally registered organization and then send the certificate via email. However, with the latest updates, all code signing certificates will be shipped to the customer on a USB device. For the existing certificate holders, they must affirm that they will use an HSM or hardware security token, a cloud-based key generation and protection solution, or a signing service that meets the requirements outlined in the CA/B Forum’s Baseline Requirements section 16.2
Extended Validation (EV) Certificates
An Extended Validation Certificate (EV) is a certificate that proves the legal entity of the owner and is signed by a certificate authority key. While it offers all the benefits of an OV certificate, it improves user trust by creating a reliable image of the publisher of the software
What are Email signing Certificates?
An email signing certificate is a type of X.509 digital certificate used to secure data for email users. Also called the S/MIME certificate, it is a useful tool that improves the security of business and personal digital information. Some users also use personal authentication certificates to refer to the certificate. It is like a modern version of an stamped letter that has not been modified by any third party. Well, not completely, but it helps people send emails securely.
An email certificate uses public key infrastructure (PKI) to:
- Allow users to sign their emails digitally so that their identity can be verified through a trusted third party, certificate authority (CA) attestation.
- Allow users to encrypt the entire contents (texts, attachments, etc.) of their emails so that the information is secure before going from server to server across the internet. It helps in protecting confidential data from man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
What are the Different Types of Email Signing Protocols?
- S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
It is built into most OSX and iOS devices and is based on a centralized authority to pick the encryption algorithm. As it is built into big web-based email companies such as Outlook and Apple, S/MIME has gained credibility and is widely used.
- PGP/MIME (Pretty Good Privacy/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
This protocol is made from a decentralized trust model and addresses security issues that deal with plain text messages. With this model in place, the users gain more flexibility and control over how properly they want their emails to be encrypted. However, the catch here is that it demands a third-party encryption tool.
These are two types of email signing protocols. Now that you know about both, let us see the similarities between email signing certificates and code signing certificates.
Similarities Between Code Signing Certificate and Email Signing
To some extent, one can tell that both certificates are similar. It is because both are used to prove that the information or content which can be anything from email to software package to document, has arrived from an authentic entity and is not modified by any third party. Let us list down some of them:
Member of the same Family
Code signing and Email signing certificates are the digital certificates belonging to the group of x.509 and are based on PKI (Public Key Infrastructure).
Strict Vetting Process
The applicants of the certificates undergo a strict vetting process conducted by a reliable certificate authority.
Protects Cybercrimes
Both of them are used as a protective shield for protecting the victims of cybercrimes.
Similar Expiry Time
Both of them offer an expiry time of one year, two years, and three years.
The similarities mentioned above are the reason why people use the term code designing software and email signing certificate interchangeably. However, there are a considerable amount of differences between the two. Let us see what they are:
What is the Difference Between Code Designing Certificate and Email Signing Certificate?
Security Coverage
When it comes to security coverage, code designing certificates are responsible for securing a wide range of applications, software, scripts, device drivers, and executable files. However, the latter secure emails, Adobe software, Microsoft Office applications, OpenOffice, LibreOffice, Apache, and other document files.
Areas of Application
While code designing certificates are used by software publishers or developers, the email signing certificates are used by Governments Entities, organizations, educational institutes, and financial institutions.
Signature Issuance
In terms of the number of signatures, code designing certificates offer an unlimited number of signatures, whereas email signing certificates offer signatures based on the type, whether an individual or organization and the certificate authority.
Application after Expiry
Upon expiry, it is not possible to sign any new executable files or software with a code designing certificate, but the past signatures, time-stamped at the time of signing, will stay valid and won’t display any warning message. In the case of an email signing certificate, after expiry, though the signature will be considered valid, one cannot sign any new emails or documents.
There you have it!
Code Signing Certificate Vs Email Signing Certificate
What does it secure?
Code Signing Certificate is works on securing:
- Applications
- Scripts
- Software
- Executable (.exe files)
- Device Drivers
Whereas Email Signing Certificate is works on securing:
- Emails
- Adobe, Microsoft Office, OpenOffice, LibreOffice, Apache, and other document files.
Supporting Users:
Code Signing is for Developers or Software publishers Whereas Email Signing is for Banks Organizations, Universities, Governments Entities
Types: of Validation:
Code Signing Supports Two types of validation includes:
- Extended Validation
- Standard Validation (Individual or Organization Code Signing Certificate)
Email Signing Supports Three types of validation includes:
- Domain Control
- Identity Verification
- Organization Validation
Number of Signature Allowed:
Code Signing offers Unlimited signatures whereas Email Signing offers number of signatures is based on certificate authority or whether it’s an individual body or organization type.
After Certificate Expiry:
After the expiry of the validity period of a code signing, it is not possible to sign new executable files and softwares. However, if your past signatures were time-stamped at the time of signing, they will stay valid and will not show any kind of warning message. Whereas, in Email Signing after the expiry of the validity period, though the signature will be considered valid, you cannot sign any new emails or documents.
Assurance:
Code Signing assures the end-users that they can rely on a particular software they have downloaded and other executable files and Email signing assures the end-users that the email or the document they are accessing has been received from a valid, authentic source without getting tampered with by any third party.
Conclusion
In a digital era that we thrive in today, nothing is possible without software, emails, or documents. Due to this important reason, the application of valid digital signatures has become inevitable. This helps the users believe that whatever software, email, or file attachment they are downloading or have downloaded has safely come from a legit entity.
While both email signing and code signing certificates are quite different at various levels, they are also like each other. Therefore, we hope that we have addressed the confusion about both certificates.

