WHAT IS THE PROCESS OF MAKING PCBs?
To assure the performance of the end product, a complicated process is needed throughout the printed circuit board PCB Assembly Process. Although circuit boards might be single, double, or multilayered, the manufacturing methods are the same up to the creation of the first layer. Some PCBs may take 20 or more stages throughout the manufacturing process due to changes in the PCB’s construction.
The complexity of printed circuit boards is inversely correlated with the number of processes needed to produce them. Any step that is skipped or the process is shortened might have a detrimental effect on the circuit board’s performance. However, the PCBs should effectively carry out their functions as essential electrical components after the project is finished.
What components make up a PCB?
A PCB is composed of four major components:
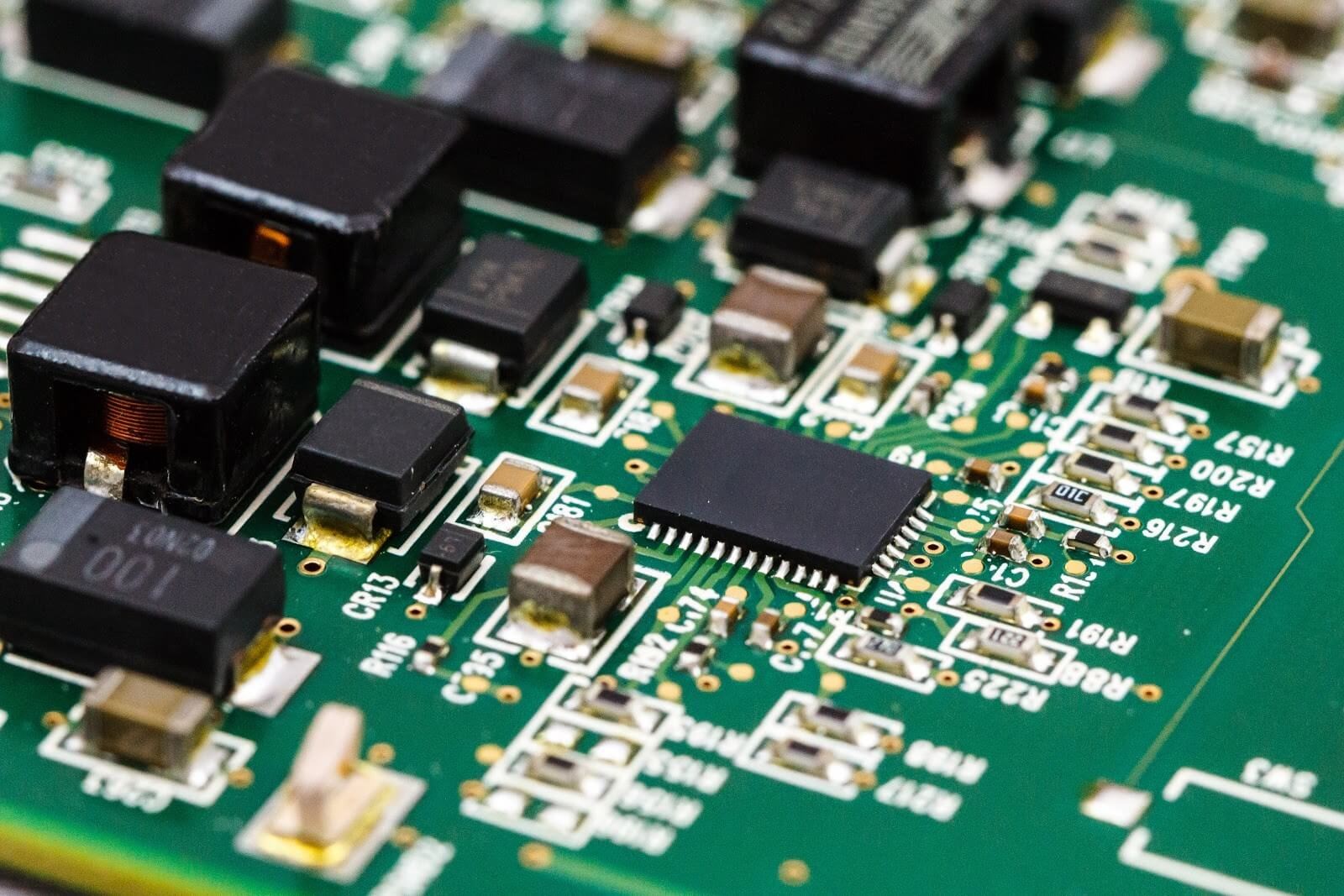
Substrate: The substrate material, which is typically constructed of fiberglass, is the first and most crucial component. Fiberglass is employed because it gives the PCB a core strength and aids in resistance to fracture. Consider the substrate as the “skeleton” of the PCB.
Depending on the kind of board, the copper layer may be either copper foil or a complete copper covering. Whatever method is used, the copper’s purpose will always be the same: to transmit electrical messages to and from the PCB, just as your nervous system transmits information from your brain to your muscles.
The third component of the PCB Assembly Process is called the solder mask, which is a polymer layer that helps shield the copper from the environment to prevent short-circuiting. The solder mask serves as the “skin” of the PCB in this fashion.
Silkscreen: The silkscreen is the last component of the circuit board. Part numbers, logos, switch settings, component references, and test points are often shown on the silkscreen on the component side of the board. The legend or nomenclature may also be called the silkscreen.
WHERE AND HOW IS A PCB MADE?
The design and verification phases of the PCB design process are followed by the production of the circuit boards. To guarantee precision and avoid short circuits or incomplete circuits, several stages need computer supervision and machine-driven equipment. Before being packed and sent to clients, the finished boards must pass rigorous testing.
First, create the PCB.
Of course, the design comes first in any PCB Assembly Process. PCB production and design always begin with a plan: the designer draws out a layout for the PCB that complies with all of the specifications. Extended Gerber, sometimes referred to as IX274X, is the most widely used design tool among PCB designers.
Extended Gerber is a great piece of software for PCB design since it also functions as an output format. Extended Gerber encrypts all the information required by the designer, including the number of copper layers, required solder masks, and additional component nomenclature. All the various components and features of the design are verified thoroughly to ensure there are no problems once the Gerber Extended program has encoded a design blueprint for the PCB.
After the designer has done reviewing it, the final PCB design is forwarded to a PCB Assembly Process firm so that the PCB may be constructed. The PCB design plan goes through a second inspection by the fabricator upon arrival at the PCB Assembly Process facility. This inspection is referred to as a Design for Manufacture (DFM) check. A thorough DFM assessment guarantees that the PCB design satisfies the minimal manufacturing tolerances. Following that, it is prepared for the design review and engineering questions that come next in the design process of Electronics Manufacturers.